- Published on
JMX in Camel Quarkus Native Mode
- Authors

- Name
- James Netherton
Camel Quarkus 3.2.0 introduced the capability to manage and monitor Camel Quarkus native applications with JMX, thanks to the experimental JMX support that was added in GraalVM 17/20 & Mandrel 23.0.
Enabling Camel JMX
Activating JMX in Camel Quarkus can be done by adding the camel-quarkus-management extension to your project.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-quarkus-management</artifactId>
</dependency>
The management extension will automatically enable Camel JMX support and will expose some useful MBeans so that we can interrogate their attributes and invoke operations.
Adding the extension to your project is enough for the normal JVM mode. In native mode, some additional configuration is required in application.properties.
quarkus.native.monitoring=jmxserver,jvmstat
This instructs the GraalVM compiler that to expose the JMX server. By default it is disabled.
This configuration can be tested with the following example project.
https://github.com/jamesnetherton/camel-quarkus-demos/tree/main/jmx-native
Clone the project and build the native executable. If you don't have GraalVM installed locally, then you can perform the native build within a container by appending the option -Dquarkus.native.container-runtime=docker to the command below.
mvn package -Dnative
Viewing Camel JMX MBeans
Run the native application using the command below.
target/*-runner -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=9996 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
A timer endpoint will fire every 5 seconds and output a message to the console.
INFO [route1] (Camel (camel-1) thread #1 - timer://tick) Hello World!
To connect to the running application via JMX, we will use JConsole. To start JConsole run the following from the command line.
jconsole
A dialog window will open listing the available JVM processes that you can connect to. The running application will be listed as io.quarkus.runner.GeneratedMain.
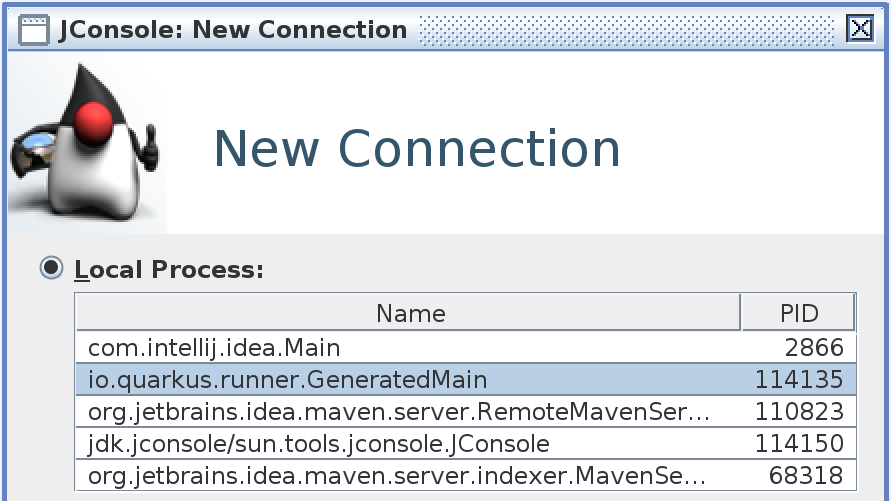
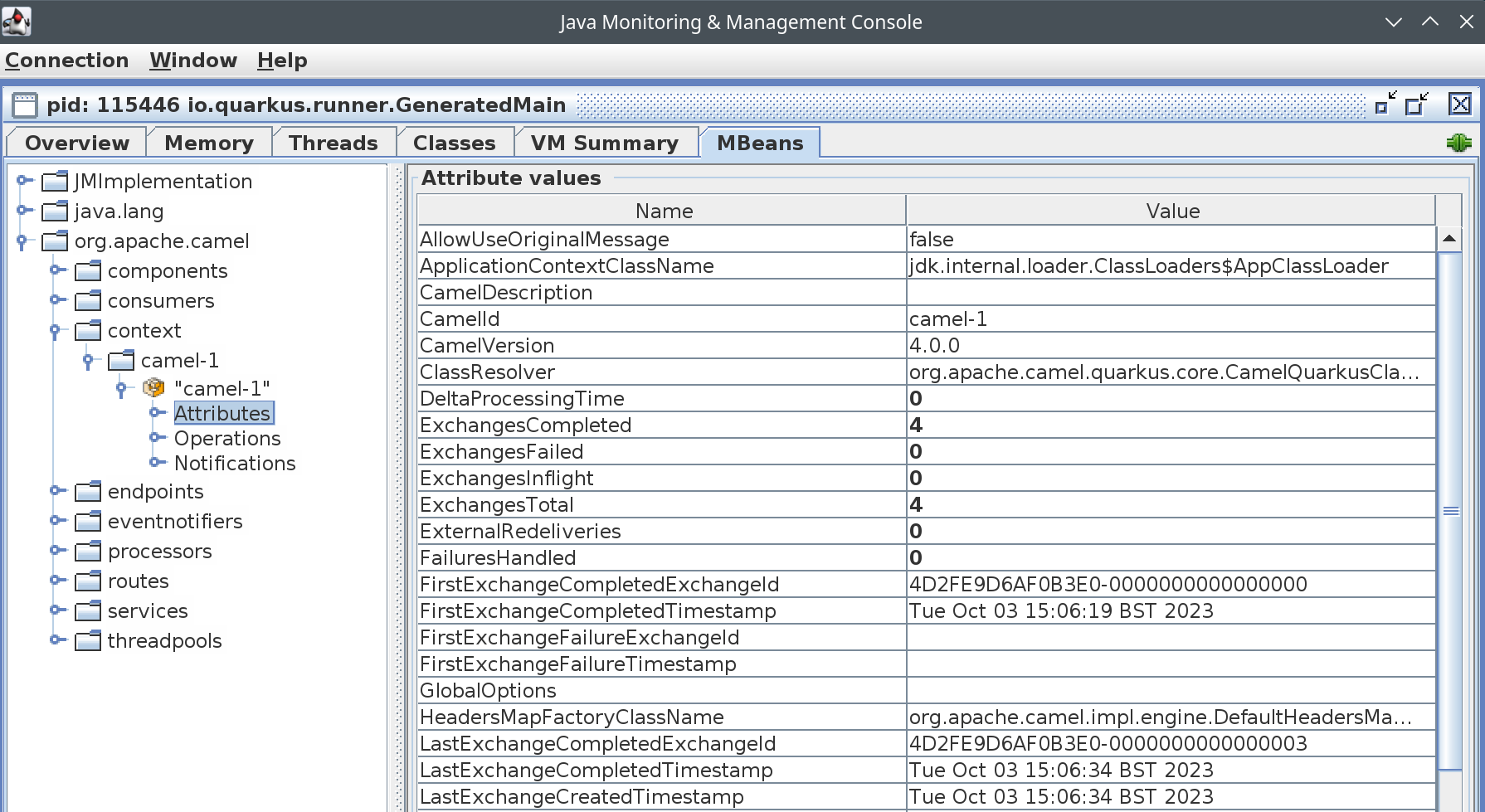
Select it and click 'Connect'. Once connected, select the 'MBeans' tab. Navigate through the MBean tree and locate the org.apache.camel parent node. Expand the node and you will see the various different MBeans that Camel JMX has exposed. If you browse through the context node, you can view some attributes and statistics related to the the Camel Context
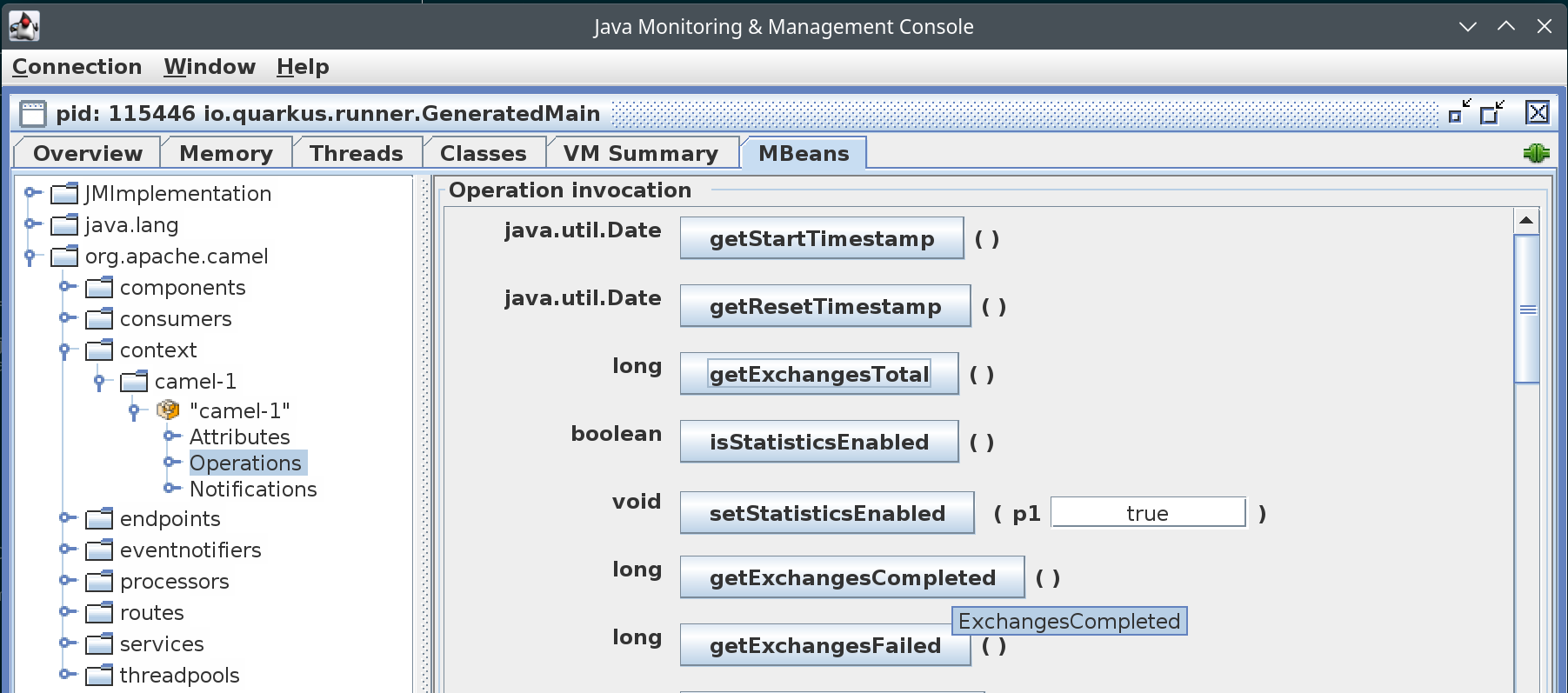
Select operations and you will see the list of available operations that can be invoke on the Camel Context. For example, click on the getExchangesCompleted button.
We can also perform management operations like suspending the Camel Context. Scroll to the end of the operations list and click the suspend button. You should notice that the console output from the timer route has stopped and a log message exists like the following.
INFO [org.apa.cam.imp.eng.AbstractCamelContext] (RMI TCP Connection(1)-127.0.0.1) Apache Camel 4.0.0 (camel-1) is suspending
INFO [org.apa.cam.imp.eng.AbstractCamelContext] (RMI TCP Connection(1)-127.0.0.1) Apache Camel 4.0.0 (camel-1) is suspended in 0ms
Click the resume button to restart the Camel routes. The console output will contain some entries like.
INFO [org.apa.cam.imp.eng.AbstractCamelContext] (RMI TCP Connection(1)-127.0.0.1) Resumed 1 routes
INFO [org.apa.cam.imp.eng.AbstractCamelContext] (RMI TCP Connection(1)-127.0.0.1) Apache Camel 4.0.0 (camel-1) resumed in 0ms
Note if you choose to stop the Camel Context, then you'll not being able to perform any further management operations, as the Camel JMX services will be shut down.
Conclusion
This brief overview shows how you can interrogate and even modify your Camel Quarkus native application at runtime. The Camel JMX Guide has more details about JMX support in Camel.
Happy coding!